Understanding Your Health Insurance Benefits
As the direction and focus of healthcare in the nation progresses, this has also left many people feeling as though they are slightly bewildered by what this means for paying for these actual care services. Further, insurance options have become far more diverse, especially as individuals and businesses consider cost effective ways to approach this situation. For the most part, many people simply decide on an option for insurance that the employer provides, although it is wise that even that process for selection is done with knowledge.
Deciphering Health Insurance Plans
It is also important to understand what type of insurance provider is being used, as this can also vastly change the benefits that are afforded. Traditional plans consist of Health Management Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), both of which have a similar structure and function, although the short-term and long-term costs of either can greatly vary.
HMOs are one of the oldest forms of coverage, and were essentially developed to help manage the rising cost of health care in the 1930s. This type of insurance is based on statistical and fiscal analysis of health needs and costs for the general population, with coverage for care that is considered necessary to maintain wellbeing. HMOs also function strongly within a network of providers, which can be limiting for some people.
The concept of networks simply refers to an agreement that the HMO or PPO has made with a set of physicians, hospitals, and other care providers, who agree to a certain pricing scale for patients with that particular insurance. Regardless of the type of plan, in network and out of network considerations should also help to inform individuals about which insurance benefits will be a best fit.
- In network – this refers to any health service provider who is included within the insurance company’s agreement. In network services will be covered by the insurance provisions. This can include some specialists in PPO networks, but tends to be limited to urgent and emergency care as well as general preventive care.
- Out of network – this simply refers to any provider that is not within the insurance organization’s list of accepted health care professionals. In some cases, paying for out of network simply means that the services are out of pocket, although HMOs require a referral in order to see an out of network provider.
PPOs are also a network based insurance program, although the preferred provider designation also means that more specialists are included within the network. Further, with a PPO plan, individuals do not need to gain a referral before seeing an out of network provision. However, since PPOs do include specialty medicine, they can have a higher premium.
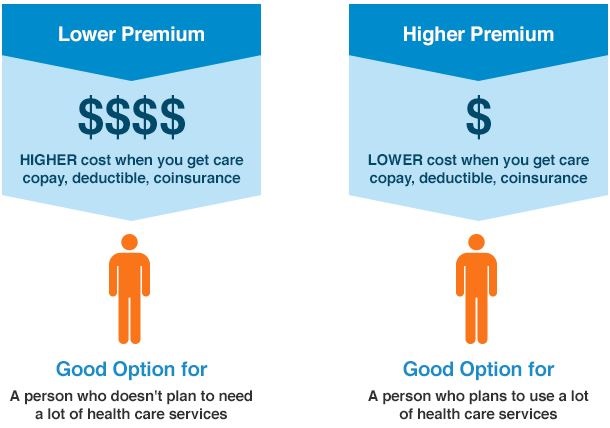
How the Premium and Deductible Can Affect Care Costs
Many employers will still offer HMO plans, as these can be some of the easiest to understand in terms of benefits and can afford a lower overall price to both the employer and the employees. However, these plans are also tiered to give purchasers a greater cost benefit given their needs. Traditionally, HMOs tend to have a low or no premium, but can also have a much higher deductible.
- Premium – this is the monthly cost for the health insurance only. Regardless of whether the insurance is used or not, individuals are still responsible for paying their premium every month.
- Deductible – this is the amount that is paid for health services, before the insurance will begin to cover care costs. Some providers will pay a percentage before the deductible is met, although the amount that the insurance carrier pays after the deductible is considerably higher.
For many people who do not have preexisting conditions and are generally healthy, choosing a plan with a low premium can be appropriate. However, it is also important to bear in mind that low or no premium will tend to mean a higher deductible, since this becomes an issue in the event of sudden chronic health needs.
This also means that for the most part, the person will have to pay out of pocket, until the deductible is met. As an example, if a person has a $2,000 deductible, they will be paying for the entirety of care costs until they have expended that $2,000 limit. This also means that with higher deductibles, more of the care costs will become the individual’s responsibility.
Many plans that have higher premiums will also have lower deductibles. While this is especially true for PPOs, it can ably to some of the higher tiers in HMO plans as well. For many individuals who have existing conditions, require a specialist, or have regular prescription costs, the trade-off of a higher monthly premium is off-set by having the insurance coverage kick in far more quickly.
What is the Difference Between Co-Pay and Co-Insurance?
Other considerations of what insurance benefits are actually offering can also help people to make the best decision about coverage that will meet actual health needs. Three terms that are often confused include:
- Out of pocket – this simply refers to what a person is paying care providers from their own budget. Out of pocket costs can include person’s co-pay, but the term covers any fees that are not paid or reimbursed through the insurance provider.
- Co-pay – this is a fixed fee that is paid for health services, as per the insurance provider’s agreement with in network health care professionals. The fee can be a certain percentage of the specific care costs, but it can also be a set dollar amount that may vary based on the type of service that is provided.
- Co-insurance – this is what kicks in once a deductible is met and refers to the amount that the insurance provider and the individual agree to pay. This tends to be a percentage of the service fees, although the ratio of what the individual actually pays is lower than that of the insurance company.





